Within the last edition of The 1.x files, we did a fast re-cap of the place the Eth 1.x analysis initiative got here from, what’s at stake, and what some attainable options are. We ended with the idea of stateless ethereum, and left a extra detailed examination of the stateless consumer for this submit.
Stateless is the brand new path of Eth 1.x analysis, so we’ll do a reasonably deep dive and get an actual sense of the challenges and prospects which are anticipated on the street forward. For people who wish to dive even deeper, I will do my greatest to hyperlink to extra verbose sources each time attainable.
The State of Stateless Ethereum
To see the place we’re going, we should first perceive the place we’re with the idea of ‘state’. After we say ‘state’, it is within the sense of “a state of affairs”.
The whole ‘state’ of Ethereum describes the present standing of all accounts and balances, in addition to the collective reminiscences of all sensible contracts deployed and operating within the EVM. Each finalized block within the chain has one and just one state, which is agreed upon by all contributors within the community. That state is modified and up to date with every new block that’s added to the chain.
Within the context of Eth 1.x analysis, it is vital not simply to know what state is, however the way it’s represented in each the protocol (as outlined within the yellow paper), and in most consumer implementations (e.g. geth, parity, trinity, besu, and so on.).
Give it a trie
The information construction utilized in Ethereum known as a Merkle-Patricia Trie. Enjoyable truth: ‘Trie’ is initially taken from the phrase ‘retrieval’, however most individuals pronounce it as ‘attempt’ to differentiate it from ‘tree’ when talking. However I digress. What we have to learn about Merkle-Patricia Tries is as follows:
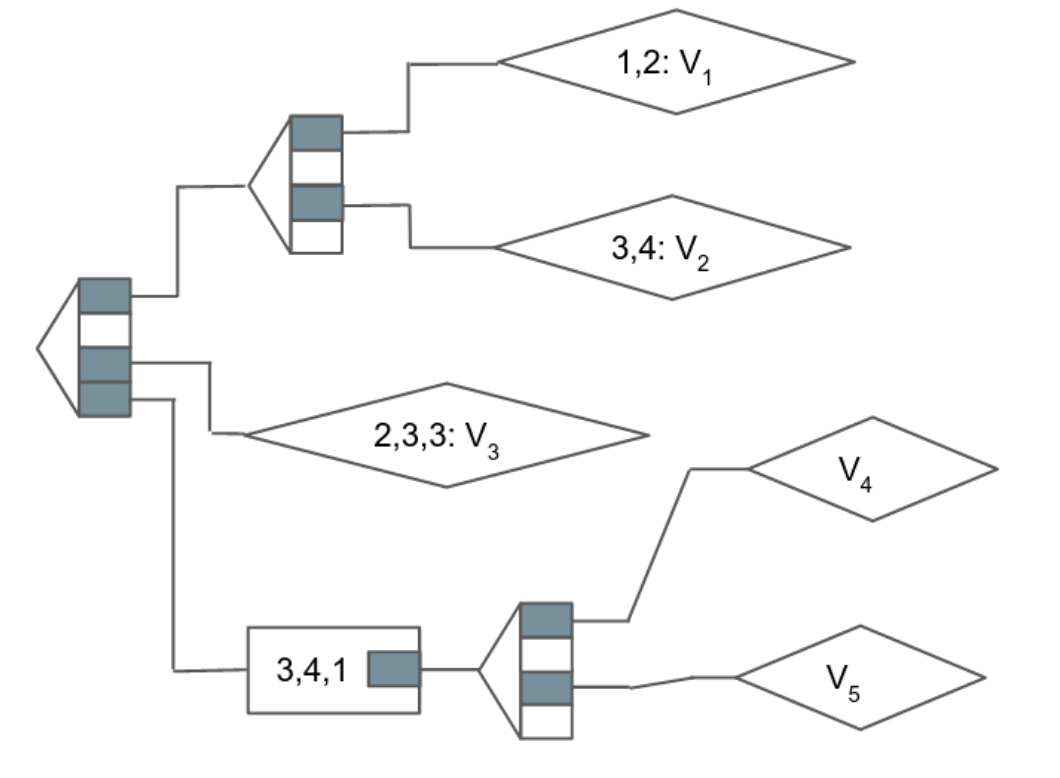
At one finish of the trie, there are all the explicit items of information that describe state (worth nodes). This could possibly be a selected account’s steadiness, or a variable saved in a wise contract (reminiscent of the whole provide of an ERC-20 token). Within the center are department nodes, which hyperlink all the values collectively by way of hashing. A department node is an array containing the hashes of its little one nodes, and every department node is subsequently hashed and put into the array of its mum or dad node. This successive hashing ultimately arrives at a single state root node on the opposite finish of the trie.
Within the simplified diagram above, we will see every worth, in addition to the path that describes methods to get to that worth. For instance, to get to V-2, we traverse the trail 1,3,3,4. Equally, V-3 could be reached by traversing the trail 3,2,3,3. Be aware that paths on this instance are all the time 4 characters in size, and that there’s usually just one path to take to achieve a worth.
This construction has the vital property of being deterministic and cryptographically verifiable: The one approach to generate a state root is by computing it from every particular person piece of the state, and two states which are an identical could be simply confirmed so by evaluating the basis hash and the hashes that led to it (a Merkle proof). Conversely, there isn’t a approach to create two completely different states with the identical root hash, and any try to change state with completely different values will lead to a distinct state root hash.
Ethereum optimizes the trie construction by introducing just a few new node sorts that enhance effectivity: extension nodes and leaf nodes. These encode components of the path into nodes in order that the trie is extra compact.
On this modified Merkle-Patricia trie construction, every node will result in a alternative between a number of subsequent nodes, a compressed a part of a path that subsequent nodes share, or values (prepended by the remainder of their path, if needed). It is the identical knowledge and the identical group, however this trie solely wants 9 nodes as an alternative of 18. This appears extra environment friendly, however with the good thing about hindsight, is not really optimum. We’ll discover why within the subsequent part.
To reach at a selected a part of state (reminiscent of an account’s present steadiness of Ether), one wants to begin on the state root and crawl alongside the trie from node to node till the specified worth is reached. At every node, characters within the path are used to determine which subsequent node to journey to, like a divining rod, however for navigating hashed knowledge constructions.
Within the ‘actual’ model utilized by Ethereum, paths are the hashes of an deal with 64 characters (256 bits) in size, and values are RLP-encoded data. Department nodes are arrays that comprise 17 parts (sixteen for every of the attainable hexadecimal characters, and one for a worth), whereas leaf nodes and extension nodes comprise 2 parts (one partial path and both a worth or the hash of the following little one node). The Ethereum wiki is probably going one of the best place to read more about this, or, if you want to get method into the weeds, this article has an excellent (however sadly deprecated) DIY trie train in Python to play with.
Stick it in a Database
At this level we must always remind ourselves that the trie construction is simply an summary idea. It is a method of packing the totality of Ethereum state into one unified construction. That construction, nonetheless, then must be carried out within the code of the consumer, and saved on a disk (or just a few thousand of them scattered across the globe). This implies taking a multi-dimensional trie and stuffing it into an unusual database, which understands solely [key, value] pairs.
In most Ethereum shoppers (all besides turbo-geth), the Merkle-Patricia Trie is carried out by creating a definite [key, value] pair for every node, the place the worth is the node itself, and the hot button is the hash of that node.
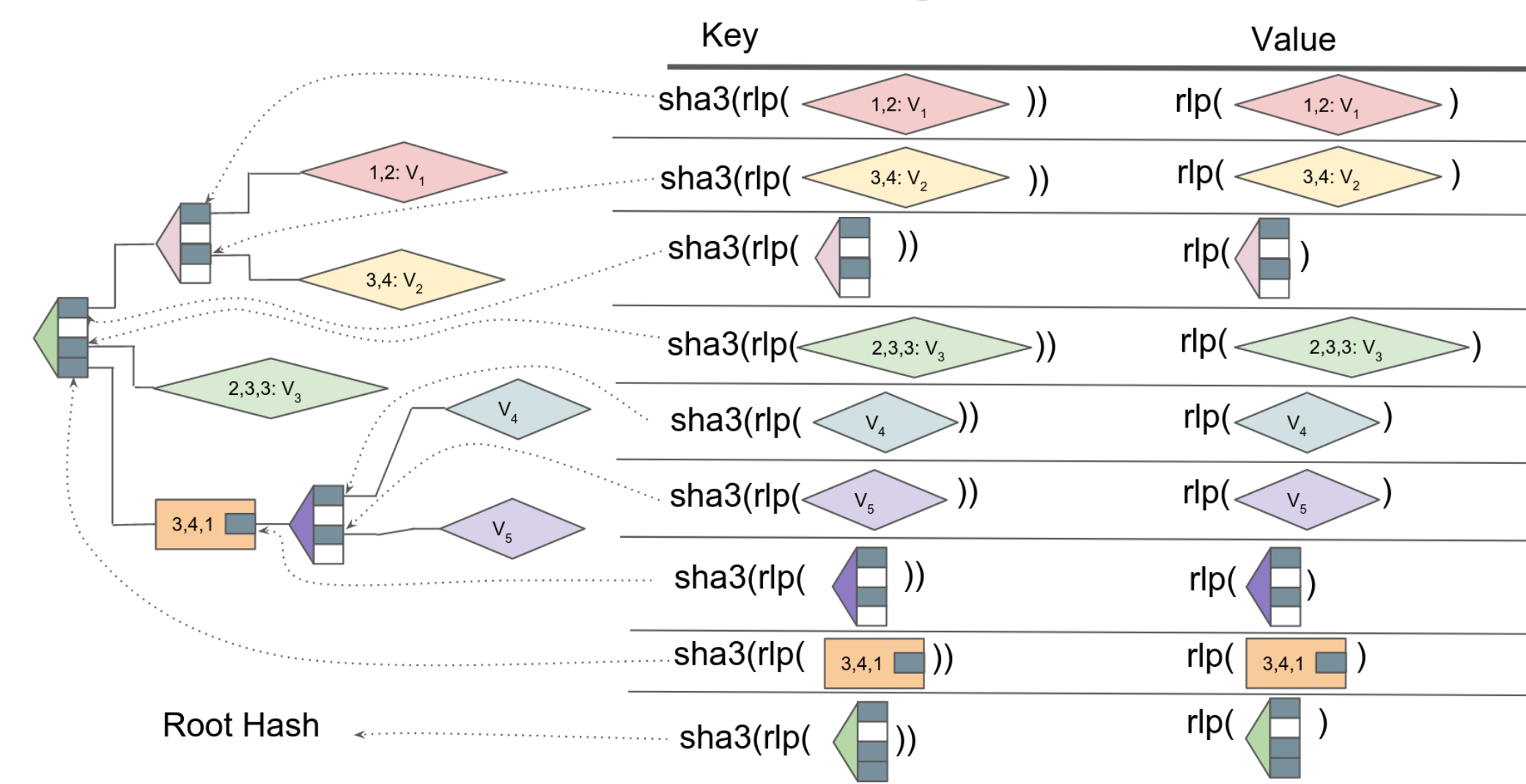
The method of traversing the trie, then, is kind of the identical because the theoretical course of described earlier. To lookup an account steadiness, we’d begin with the basis hash, and lookup its worth within the database to get the primary department node. Utilizing the primary character of our hashed deal with, we discover the hash of the primary node. We glance that hash up within the database, and get our second node. Utilizing the following character of the hashed deal with, we discover the hash of the third node. If we’re fortunate, we would discover an extension or leaf node alongside the best way, and never have to undergo all 64 nibbles — however ultimately, we’ll arrive at our desired account, and be capable to retrieve its steadiness from the database.
Computing the hash of every new block is basically the identical course of, however in reverse: Beginning with all the sting nodes (accounts), the trie is constructed by way of successive hashings, till lastly a brand new root hash is constructed and in contrast with the final agreed-upon block within the chain.
This is the place that bit concerning the obvious effectivity of the state trie comes into play: re-building the entire trie may be very intensive on disk, and the modified Merkle-Patricia trie construction utilized by Ethereum is extra protocol environment friendly at the price of implementation effectivity. These additional node sorts, leaf and extension, theoretically save on reminiscence wanted to retailer the trie, however they make the algorithms that modify the state contained in the common database extra advanced. After all, a decently highly effective laptop can carry out the method at blazing pace. Sheer processing energy, nonetheless, solely goes to date.
Sync, child, sync
To this point we have restricted our scope to what is going on on in an particular person laptop operating an Ethereum implementation like geth. However Ethereum is a community, and the entire level of all of that is to maintain the identical unified state constant throughout 1000’s of computer systems worldwide, and between completely different implementations of the protocol.
The continuously shuffling tokens of #Defi, cryptokitty auctions or cheeze wizard battles, and unusual ETH transfers all mix to create a quickly altering state for Ethereum shoppers to remain in sync with, and it will get tougher and tougher the extra well-liked Ethereum turns into, and the deeper the state trie will get.
Turbo-geth is one implementation that will get to the basis of the issue: It flattens the trie database and makes use of the trail of a node (reasonably than its hash) because the [key, value] pair. This successfully makes the depth of the tree irrelevant for lookups, and permits for quite a lot of nifty options that may enhance efficiency and cut back the load on disk when operating a full node.
The Ethereum state is huge, and it adjustments with each block. How huge, and the way a lot of a change? We are able to ballpark the present state of Ethereum at round 400 million nodes within the state trie. Of those, about 3,000 (however as many as 6,000) should be added or modified each 15 seconds. Staying in sync with the Ethereum blockchain is, successfully, continuously constructing a brand new model of the state trie time and again.
This multi-step means of state trie database operations is why Ethereum implementations are so taxing on disk I/O and reminiscence, and why even a “quick sync” can take as much as 6 hours to finish, even on quick connections. To run a full node in Ethereum, a quick SSD (versus an inexpensive, dependable HDD) is a requirement, as a result of processing state adjustments is extraordinarily demanding on disk learn/writes.
Right here it is vital to notice that there’s a very massive and vital distinction between establishing a brand new node to sync and holding an current node synced — A distinction that, once we get to stateless Ethereum, will blur (hopefully).
The easy approach to sync a node is with the “full sync” technique: Ranging from the genesis block, an inventory of each transaction in every block is retrieved, and a state trie is constructed. With every subsequent block, the state trie is modified, including and modifying nodes as the whole historical past of the blockchain is replayed. It takes a full week to obtain and execute a state change for each block from the start, but it surely’s only a matter of time earlier than the transactions you want are pending inclusion into the following new block, reasonably than being already solidified in an previous one.
One other technique, aptly named “fast-sync”, is faster however extra sophisticated: A brand new consumer can, as an alternative of requesting transactions from the start of time, request state entries from a current, trusted ‘checkpoint’ block. It is much less complete info to obtain, however it’s nonetheless quite a lot of info to process– sync just isn’t presently restricted by bandwidth, however by disk efficiency.
A quick-syncing node is basically in a race with the tip of the chain. It must get all of the state on the ‘checkpoint’ earlier than that state goes stale and stops being provided by full nodes (It will possibly ‘pivot’ to a brand new checkpoint if that occurs). As soon as a fast-syncing node overcomes the hurdle and get its state totally caught up with a checkpoint, it might probably then change to full sync — constructing and updating its personal copy of state from the included transactions in every block.
Can I get a block witness?
We are able to now begin to unpack the idea of stateless Ethereum. One of many major objectives is to make new nodes much less painful to spin up. On condition that solely 0.1% of the state is altering from block to dam, it looks as if there needs to be a way of chopping down on all that additional ‘stuff’ that must be downloaded earlier than the complete sync switchover.
However this is likely one of the challenges imposed by Ethereum’s cryptographically safe knowledge construction: In a trie, a change to only one worth will lead to a very completely different root hash. That is a characteristic, not a bug! It retains everyone sure that they’re on the identical web page (on the identical state) with everybody else on the community.
To take a shortcut, we want a brand new piece of details about state: a block witness.
Suppose that only one worth on this trie has modified not too long ago (highlighted in inexperienced):
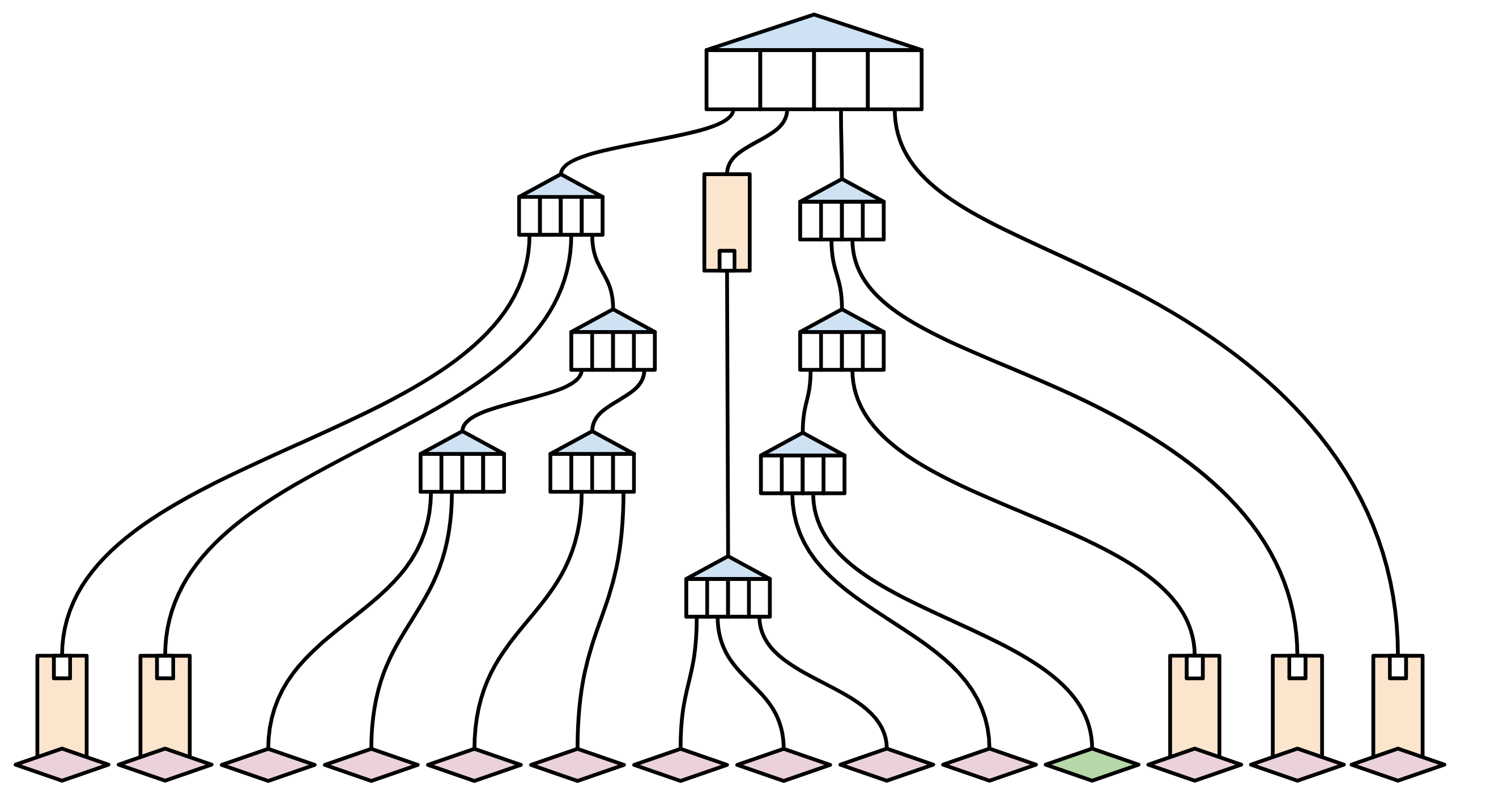
A full node syncing the state (together with this transaction) will go about it the old style method: By taking all of the items of state, and hashing them collectively to create a brand new root hash. They’ll then simply confirm that their state is similar as everybody else’s (since they’ve the identical hash, and the identical historical past of transactions).
However what about somebody that has simply tuned in? What is the smallest quantity of data that new node wants with the intention to confirm that — no less than for so long as it has been watching — its observations are in line with everybody elses?
A brand new, oblivious node will want older, wiser full nodes to offer proof that the noticed transaction matches in with the whole lot they’ve seen to date concerning the state.
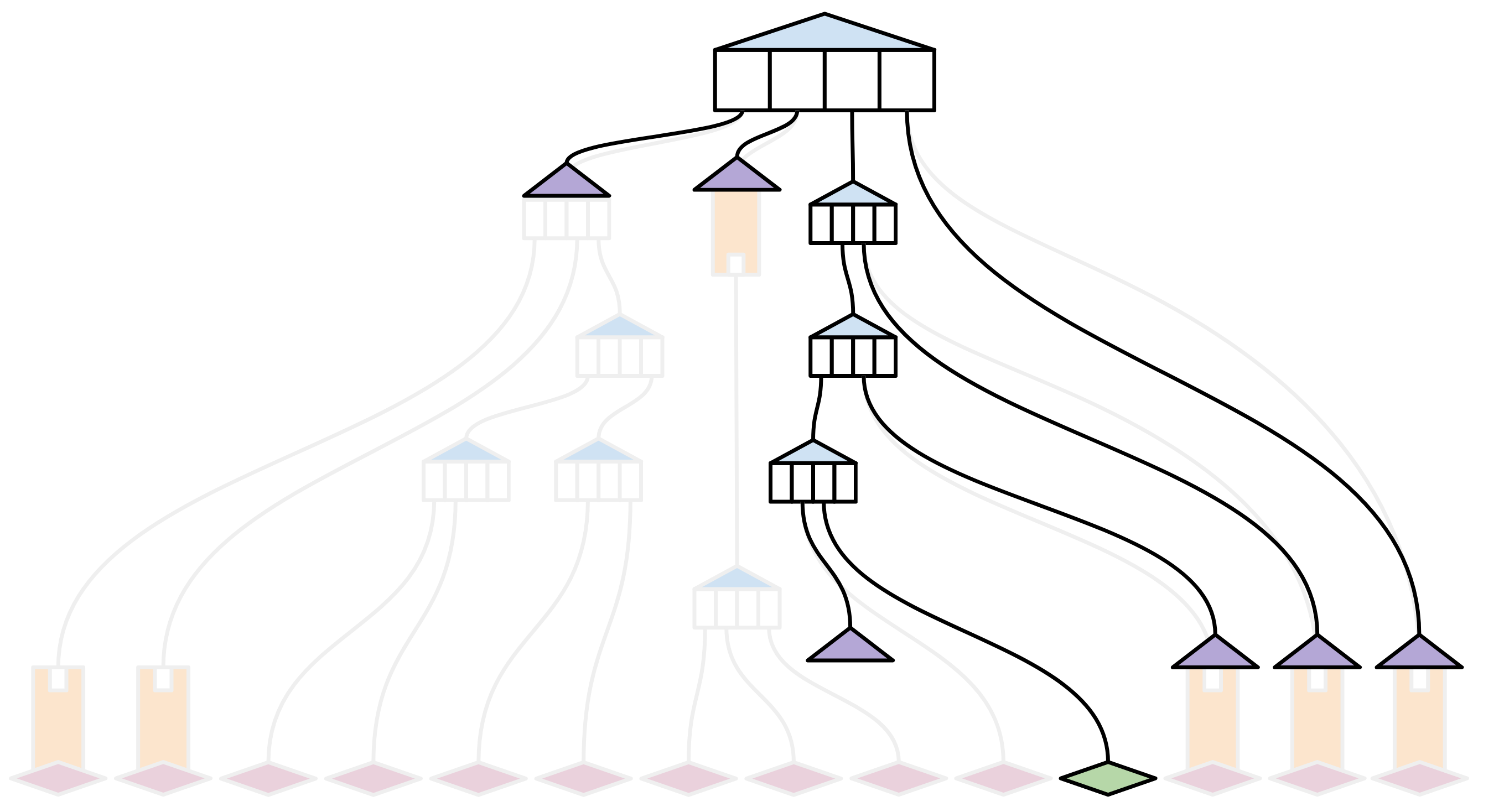
In very summary phrases, a block witness proof supplies all the lacking hashes in a state trie, mixed with some ‘structural’ details about the place within the trie these hashes belong. This permits an ‘oblivious’ node to incorporate the brand new transaction in its state, and to compute the brand new root hash domestically — with out requiring them to obtain a complete copy of the state trie.
That is, in a nutshell, the concept behind beam sync. Slightly than ready to gather every node within the checkpoint trie, beam sync begins watching and making an attempt to execute transactions as they occur, requesting a witness with every block from a full node for the data it would not have. As an increasing number of of the state is ‘touched’ by new transactions, the consumer can rely an increasing number of by itself copy of state, which (in beam sync) will steadily fill in till it will definitely switches over to full sync.
Statelessness is a spectrum
With the introduction of a block witness, the idea of ‘totally stateless’ begins to get extra outlined. On the identical time, it is the place we begin to run into open questions and issues with no apparent answer.
In distinction to beam sync, a really stateless consumer would by no means make a copy of state; it might solely seize the newest transactions along with the witness, and have the whole lot it must execute the following block.
You may see that, if the complete community had been stateless, this might really maintain up forever– witnesses for brand spanking new blocks could be produced from the earlier block. It would be witnesses all the best way down! No less than, all the way down to the final agreed upon ‘state of affiars’, and the primary witness generated from that state. That is a giant, dramatic change to Ethereum not prone to win widespread assist.
A much less dramatic strategy is to accommodate various levels of ‘statefullness’, and have a community through which some nodes maintain a full copy of the state and might serve everybody else contemporary witnesses.
-
Full-state nodes would function as earlier than, however would moreover compute a witness and both connect it to a brand new block, or propagate it by way of a secondary community sub-protocol.
-
Partial-state nodes may maintain a full state for only a brief variety of blocks, or maybe simply ‘watch’ the piece of state that they are excited by, and get the remainder of the info that they should confirm blocks from witnesses. This may assist infrastructure-running dapp builders immensely.
-
Zero-state nodes, who by definition wish to maintain their shoppers operating as gentle as attainable, may rely fully on witnesses to confirm new blocks.
Getting this scheme to work may entail one thing like bittorrent-style chunking and swarming habits, the place witness fragments are propagated in keeping with their want and greatest connections to different nodes with (complementary) partial state. Or, it’d contain figuring out an alternate implementation of the state trie extra amenable to witness era. That is stuff to analyze and prototype!
For a way more in-depth evaluation of what the trade-offs of stateful vs stateless nodes are, see Alexey Akhunov’s The shades of statefulness.
An vital characteristic of the semi-stateless strategy is that these adjustments do not essentially indicate huge, hard-forking adjustments. Via small, testable, and incremental enhancements, it is attainable to construct out the stateless part of Ethereum right into a complementary sub-protocol, or as a collection of un-controversial EIPs as an alternative of a giant ‘leap-of-faith’ improve.
The street(map) forward
The elephant within the analysis room is witness dimension. Atypical blocks comprise a header, and an inventory of transactions, and are on the order of 100 kB. That is sufficiently small to make the propagation of blocks fast relative to community latency and the 15 second block time.
Witnesses, nonetheless, have to comprise the hashes of nodes each on the edges and deep contained in the state trie. This implies they’re much, a lot larger: early numbers recommend on the order of 1 MB. Consequently, syncing a witness is far a lot slower relative to community latency and block time, which could possibly be an issue.
The dilemma is akin to the distinction between downloading a film or streaming it: If the community is just too sluggish to maintain up with the stream, downloading the complete film is the one workable choice. If the community is far sooner, the film could be streamed with no drawback. Within the center, you want extra knowledge to determine. These with sub-par ISPs will acknowledge the gravity of making an attempt to stream a friday evening film over a community that may not be up for the duty.
This, largely, is the place we begin entering into the detailed issues that the Eth 1x group is tackling. Proper now, not sufficient is understood concerning the hypothetical witness community to know for certain it’s going to work correctly or optimally, however the satan is within the particulars (and the info).
One line of inquiry is to consider methods to compress and cut back the scale of witnesses by altering the construction of the trie itself (reminiscent of a binary trie), to make it extra environment friendly on the implimentation stage. One other is to prototype the community primitives (bittorrent-style swarming) that enable witnesses to be effectively handed round between completely different nodes on the community. Each of those would profit from a formalized witness specification — which does not exist but.
All of those instructions (and extra) are being compiled right into a extra organized roadmap, which might be distilled and revealed within the coming weeks. The factors highlighted on the roadmap might be matters of future deep dives.
For those who’ve made it this far, you need to have a good suggestion of what “Stateless Ethereum” is all about, and a number of the context for rising Eth1x R&D.
As all the time, if in case you have questions on Eth1x efforts, requests for matters, or wish to contribute, come introduce your self on ethresear.ch or attain out to @gichiba and/or @JHancock on twitter.
Particular because of Alexey Akhunov for offering technical suggestions and a number of the trie diagrams.
Glad new 12 months, and blissful Muir Glacier hardfork!
